Starter
Optical Storage
Optical Storage Devices
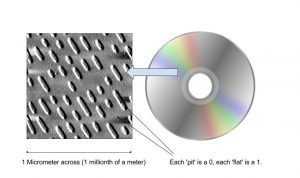
Optical storage devices work by firing a microscopic laser beam at the surface of a spinning plastic disk, such as a DVD, CD or Blu ray. The surface of the disk is a combination of flats ( representing 1s) or pits (zeros). Depending on whether the laser hits a flat or a pit the laser beam deflects differently, and this difference in deflection is recorded by a later detector.
Advantages of optical storage
- Cheap per GB of storage
- Portable – cheap and easy to post
Disadvantages of optical storage
- Easy to break
- Not always reliable
- Slow read-write speeds
This technology is used in…

CD Players

DVD Drives

Blu-ray drives
Optical Animation
Optical Storage Devices Animation
Magnetic Storage
Magnetic Storage ( Hard Drives, Tape Drives, Floppy Disks)
Can’t access YouTube? Click here for the Google Drive Version
How they work
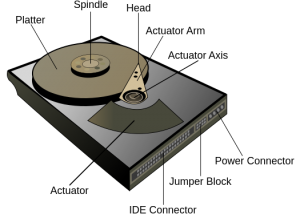
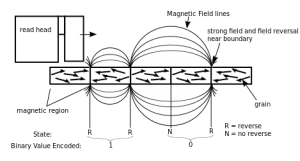
Magnetic drives work by changing the magnetic polarity of the the surface of a glass or metal platter. A read head on a actuator arm detects the polarity and the data is interpreted as either a 1 or a 0, depending on the polarity detected.
Advantages
- Very cheap per GB storage
- Medium read/write speeds
- Quite robust
Disadvantages
- Not very portable
- Can be damaged if dropped
This technology is used in…

HDD Hard Drive
Solid State Drives
Solid State Drives ( SD Cards, SSD Hard drives, Pen drives)
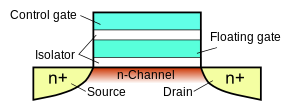
Solid state drives work by storing the data inside on microscopic silicon chips called floating gate transistors. The floating gate stores electrons, and the memory cell itself can detect if electrons are stored.
Advantages
- Fast read-write speeds – Because the data is stored directly in the silicon chip the read-write speeds are incredibly quick
- As there are no moving parts, SSDs are very robust and can withstand being dropped
Disadvantages
- They are more expensive per GB than other forms of storage
This technology is used in…

Pen Drives

SD Cards

SSD Hard Drives in smartphones and tablets