Search Algorithms
What are searching algorithms?
Search algorithms are algorithms designed to find items in an an array(list). If the item is found in the search the the algorithm will return the index(position) of the item in the array. If an array contains duplicates of an item being searched for it will normally return the index of the first instance that it finds.
Example
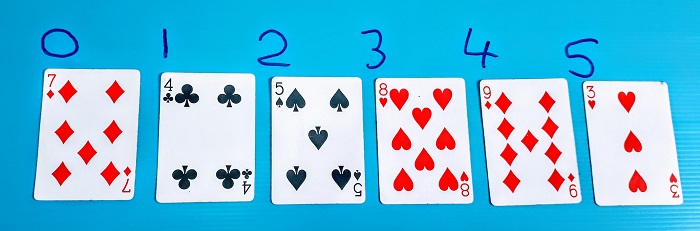
In the array of cards below , if you searched for the item ‘4 of clubs’, the algorithm would return the integer 1.
*Some languages, such as Scratch would return 2, as they start counting at 1 instead of 0.
What happens if the item is not in the array?
If the item is not found then depending on the programming different things will happen:
- Python – It will raise an exception (ERROR!!!)
- JavaScript – It will return -1 (JavaScript arrays start indexing from zero)
- Scratch – It return Zero (Scratch lists are 1 based because it’s a blocks based language designed for children)
Linear Search
Linear Search
The linear search(a.k.a sequential search) algorithm is a simple search algorithm that starts at the left hand side of an array (index 0) and moves through the array one item at a time. Once the item being searched for is found the algorithm returns the index of the item in question. If the algorithm reaches the end of the array without finding the item then it either returns an error or it returns a non valid index depending on the implementation.
Example Python Code Implementation of Linear Search
How does my implementation above differ to standard Python in the way it handles linear search?