Dictionary
Data Dictionary
As well as storing the data itself, a database also stores metadata (data about data) as well. This is stored in the data dictionary and includes:
- The names of all the tables
- The column names for all of the tables
- The data types for all the columns in each table
- Data constraints within the tables (e.g. whether a field allows a NULL value)
Modelling
Database Modelling & Schema
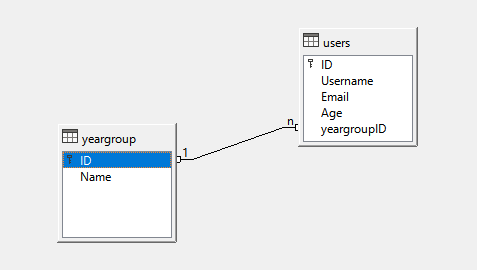
Data Modelling & Logical Schema
Data modelling can be conducted visually using a Database Management System’s in-built modelling and is an important feature of a database management system.
Views
Custom Views for different users
The database management system can be used to present different views of the database to different users.
Depending on who is accessing the database they might be able to view all data on the database, view only certain data and have write access. These views often consist of forms and reports
Form Views
Report Views
Security
Database Security & Integrity
Relational databases have a number of security advantages over flat file systems.
Automatic Backups
Relational databases can be configured to automatically backup to both local and remote storage, while preserving the database integrity. This is useful if multiple backups need to be merged to restore from a database corruption event.
Access Rights for users /groups
Individual users or groups of users can be given varying access to the database depending on their level and job role. Members of departments can be limited in what data they can access and also the nature of that access (such as read / write / execute / delete / append access). This allows for granular and compartmentalised design and control of the database system.
Query Log
Interfaces
DBMS Interfaces
There are 3 types of interfaces that the DBMS provide:
- User Interface
- Administrator Interface
- Developer Interface
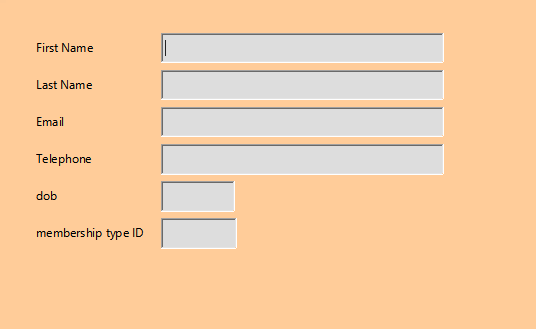
User Interface
This interface is designed for the end user. Input and viewing high controlled using User Access Levels (UAL) so that they can only view and edit data related to their account. This inter
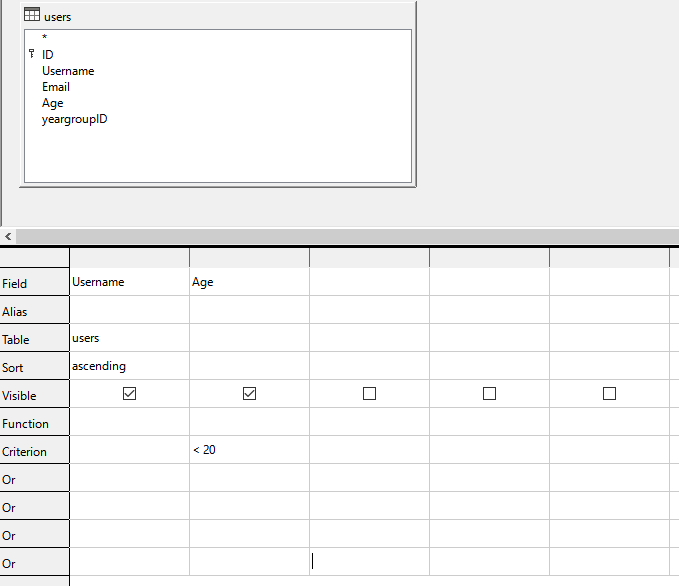
Administrator Interface
The administrator interface is designed to allow a greater amount of access and functionality than the user interface but without needed to know how to execute SQL queries.
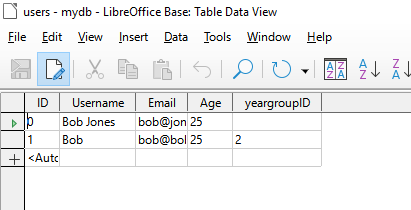
Example of the database administrator interface. Here existing tuples in the users table can be edited.
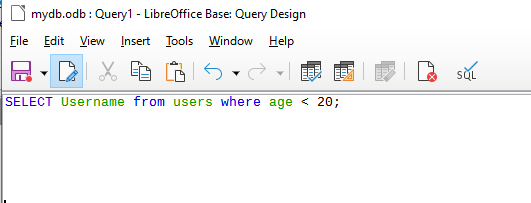
Developer Interface
Access to the developer interface allows detailed inspection of the database contents and metadata to be performed, mainly through the use of custom crafted SQL queries that can be executed within the developer interface.
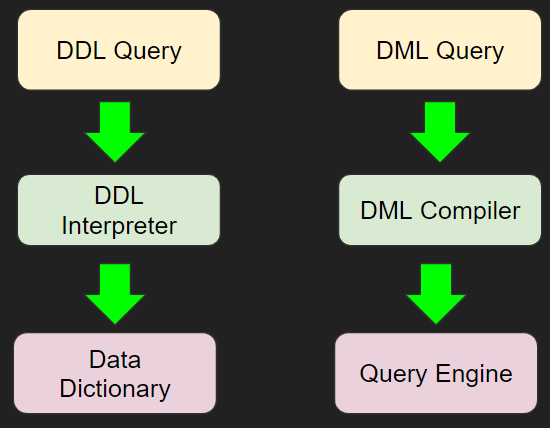
Query Processor
Query Processor
The job of the query processor is to take the query text passed to it by other modules in the DBMS, parse the data and execute it in the appropriate manner.
- DDL Queries, such CREATE & DROP, are passed to the DDL interpreter which then reads/modifies the contents of the data dictionary.
- DML Queries, such as SELECT & INSERT, are passed to the DML compiler. These queries are compiled, optimised and then executed by the query engine.