Introduction
What is Binary Coded Decimal
Binary Coded Decimal is a form of binary representation where each denary digit is converted individually into binary, rather than the whole number being converted as a large number.
Example 1 – the number 42
Normally this number would be converted directed to binary as 00101010 as 8 bit binary.
| 128 | 64 | 32 | 16 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
However in binary coded decimal we would convert the number 4 to binary and the number 2 to binary, then simply concatenate(combine) the 2 numbers together
Binary 4
| 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Binary 2
| 8 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Therefore 42 in BCD binary would be 01000010
Why use BCD?
Why use Binary Coded Decimal?
Binary coded decimal has 3 main advantages
- It is easier for a human to read large binary numbers than if the number is in pure binary
- It is simpler to create hardware than only counts in decimal and uses basic calculation (e.g. digital clocks, simple handheld calculators)
- Binary coded decimal removes the problem of floating point rounding errors, which makes is very useful for handling financial transactions.
BCD Clock Demo
Binary Coded Decimal Clock Demonstration Project
Financial systems
Financial Systems
In binary systems decimals numbers are stored using a floating point representation. When representing fractions of a whole some numbers cannot be stored accurately using binary, due to the fractions not fitting perfectly within a binary base 2 system. This results in a floating point rounding error. In financial systems rounding errors are unacceptable and must be dealt within. For this reason binary coded decimal is used instead.
Floating point rounding example
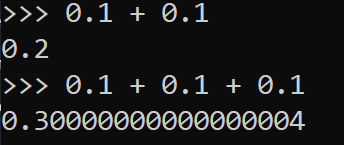
Here is a great example of a floating point binary rounding error. This kind of error is not acceptable in financial transactions.