The history of the Internet and World Wide Web
We live in a world that is surrounded by internet connected devices, many of which wouldn’t function at all without the internet. But as we become more familiar with these devices, it is easy to become separated from the technology that controls them. In this lesson we look at the history of the internet and world wide web, and the technology behind it.

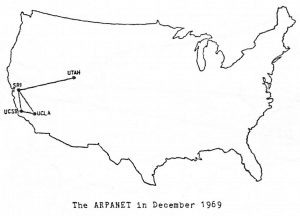
ARPANET
Born -1969
“We need to substitute for the book a device that will make it easy to transmit information without transporting material”
JCR Licklinder, Libraries of the future (Inventor of ARPANET)
ARPANET was first invented in the height of the cold war as a tool for the secure transmission of military intelligence. The system was designed so that in the event of a nuclear attack, even if one machine went down, the system would still function.
The system sent it’s first message from October 29th 1979.
Born – October 1971
In the late 1960s Ray Tomlinson, an engineer at ARPANET, was tasked with modifying the program that allowed users of the same computer to send messages to each other. His aim was to allow users to send messages to users at other machines. In 1971 he finally solved the problem and in doing so he invented the email. One key component his email system that still remains today is the @ symbol in an email address. He decided on the user@organisation email format that still remains today!
What is the Internet?
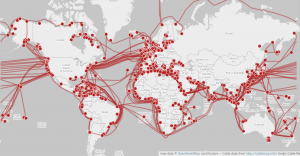
The internet is a global network of computers, all connected together through a mix of undersea cables, satellites, telephone lines and fibre-optic cables.
Common Internet Protocols include:
- TCP, IP, IMAP, POP, SMTP.
After the creation of ARPANET there sprang up a number of networks around the world, but each of these networks operated on with their own software, hardware and protocols. Because different systems used different voltages, languages and rules, they couldn’t talk to each other. In 1983 a set of rules were created (TCP and IP among others)that specified how data would be transferred between networks. This allowed different networks to communicate with other globally – the birth of the internet!
The internet hosts a number of different services, including:
- The websites and pages of the World Wide Web
- Email servers, for hosting and sending email
- File Storage and transfer
- Secure communication services
World Wide Web
What is the World Wide Web?
The World Wide Web is system that allows multiple documents (e.g. HTML documents) and files to be connected to together through the use of Hypertext links. The World Wide Web lives on the internet, but it is not the internet!
Common WWW protocols:
- HTML, HTTP, HTTPS
Throughout the 1980s the internet became increasingly popular within government, academic and business circles – with file transfer, email use and bulletin boards becoming widely used. However information sharing was still limited because users had to connect to a single source and finding information was difficult.
“In those days, there was different information on different computers, but you had to log on to different computers to get at it. Also, sometimes you had to learn a different program on each computer. Often it was just easier to go and ask people when they were having coffee…”
Source: Web foundation
Tim Berners Lee proposed a new concept that would allow for far easier information sharing. A single global langauge for information display that would work on any machine. The key feature of this new system was that each page could contain links to another page – hence the term web.
He developed two key protocols:
- HTTP – Hyper Text Transfer Protocol – How web pages would be sent access the internet.
- HTML – Hyper Text Markup Language – How web pages would be displayed when they got there.

Hyper Text Markup Language is the main language of the World Wide Web.
Networking Protocols ( Standards)
Each of the internet services above need to communicate with each other using an agreed language, called a Protocol. If they all used different protocols, none of the services would be able to work together.
Example Protocols
| Function | Protocol | Protocol Full Name |
| Display a webpage | HTTPS | Hyper Text Transfer Protocol |
| Display a webpage securely | HTTPS | Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure |
| Send an email | POP | Post Office Protocol |
| ” ” “” | SMTP | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol |
| Transfer Files | FTP | File Transfer Protocol |
| Transfer files securely | FTPS | File Transfer Protocol Secure |
Image source : http://bit.ly/2cJBf5Z
history-of-the-www-and-internet-worksheet
Watch the videos in the videos section and complete the attached worksheet.