Introduction
The analysis phase is split in to 4 parts.
- Project brief
- Research
- Description of the current system
- Specification of the new system.
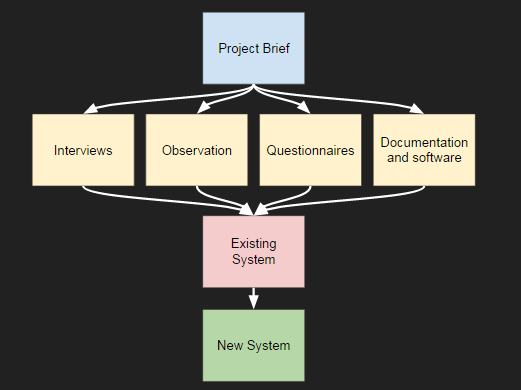
Analysis phase flow diagram
Project Brief
The project brief is usually written by the head of the project, after an initial meeting with the client. It may also be provided by the client and is used to guide the initial research.
Observation
Observation
Observation is where an person or persons goes in to the business premises and watches how users interact with the present system. They will then takes notes on the system and usually produce an observation report. This report might include:
- Detailed description of the inputs, processes and outputs of the current system.
- Descriptions of how users interact with the current system
- Limitations and inefficiencies of the current system.
Observation is often used before any interviews and questionnaires, as it often raises a number of questions that can be explored further in detail.
- Not a lot of preparation required, so can be done early on in a project.
- A rich and detailed picture of the current system can be gathered.
- Observations are relatively unbiased
- The quality and accuracy of information is highly dependent on the skill of the observer.
- People often act differently when observed, especially if they have strong positive/negative opinions in a system change.

Interviews
Interviews
In depth interviews allows the research to ask a number of exploratory and investigatory questions, going in to a great deal of depth and detail about the specifics of the current system. Interviews can be structured / semi-structured, and can cover a wide range of topics regarding the current system.
- Allows in depth qualitative questioning.
- Allows open ended feedback, where issues can raised that the interviewer may not have been aware of beforehand
- Due to the time it takes to conduct, code and write-up interviews, you can only interview a small sub-section of users, so you might not get all opinions.
- Interviews offer little quantitative data, so it is difficult to generalise from interview responses.
Questionnaires
Questionnaires
Questionnaires are often used to explore questions raised in the interview and observation stage, and do to their nature can be given out to a large number of users.
- They can be used to gain information from a wide number of people with little effort.
- You can generalise with confidence if enough questionnaire responses are received.
- Not all respondents will answer fully / at all.
- Information received is limited to the questions asked, and many questions could be overlooked.
- Paper-based questionnaires take a long time to collate, code and analyse.

Documents
Analysis of documentation and software
Another important technique is analyse documents from the current system, this can include:
- Technical manuals
- Training manuals.
- User manuals
Other documents, such as email memos
- Documents should highlight the current workflow – inputs, process and outputs.
- Technical documents will be invaluable in the design of the new system.
- The documents may be inaccurate / out of date.
- The documents are unlikely to highlight the inefficiencies of the existing system.
Current system
Description of the Current System
Once your research is complete you will be able to produce a full description of the current system, including:
- The inputs, processes and outputs of the current system.
- Users and stakeholders in the current system.
- Limitations of the existing system
Inputs, processes and outputs
Problems with the current system
Users  in the current system
These are people who interact directly with the system.
- Teachers – inputting registration
- Students – checking online if they have any homework
- Parents – view the child’s performance / attendence data
- Admin staff – sending letters to parents
- Management staff  – looking at whole school performance and attendance
Stakeholders in the current system
These are people who direct interact directly in the system, but are connected with the system in some way:
- Governers of the school – would want to know the school performance.
- Inspectors of the school – need to know certain pieces of data
New system
New System Specification
You can then finally go on to produce a specification of the new system, this specification is then used by the design team to design the software.
The specification details:
- What the new system needs to be able to do.
- Who are the users of the new system.
- What parameters the new system needs to operate within.
Resources
Teacher slideshow for the lesson.
Part 1 – fill out the first table on the worksheet, using data the you can find on the page.
Part 2 – Using the scenario of a school society or club, fill out the example inputs, processes and outputs of the current system.