Starter
GPS Wordsearch
What GPS applications can you find?

- AGRICULTURE
- AVIATION
- GEOCACHING
HIKING - MAPPING
- MINING
PHOTOGRAPHY - RAIL
- ROADTRANSPORT
SCIENCE - SECURITY
- SHIPPING
SURVERYING - TRACKING
- WEATHER
Introduction
Satellite Systems
The world’s first satellite ‘Sputnik’ was successfully lunch by the Soviet Union in 1957, and since then the number has increased to over 1,100 operational satellites, together with over 2000 obsolete satellites. Satellites are both military and private and orbit the earth either a geo-stationary (they stay in a fixed position above the earth) or non-geostationary orbit. The lower the orbit, the fast the orbit.
The increasing number of obsolete old satellites, together with other space debris has led to concerns that space junk may collide with space craft or other satellites.

GPS
Global Positioning Systems (GPS)
How do they work?
Global Positional Systems work in two parts. Firstly a global network of satellites constantly broadcast a time signal. Each satellite has an Atomic clock on board, a very accurate clock and broadcasts the time signal at the speed of light. The receiver receives the signal, and when it does it compares the time it took each signal to travel from the satellite to the receiver. In doing so it is able to triangulate it’s position on earth. There are over 50 GPS satellites in orbit, and at any one time a receive can usually receive signals from 6 to 8 of them ( the rest are blocked by the earth). GPS systems are usually accurate to within 5 and 50 metres.
What are they used for?
- GPS Navigation
- Vehicle tracking
- Animal migration tracking
- GEO-location services
Sat Nav
Satellite Navigation Systems (SatNav)
Satellite Navigation systems use a combination of GPS and GIS data to help a  user navigate around a physical space.
They are commonly used for:
- Road vehicle navigation
- Airplane navigation
- Missile navigation (in conjunction with other technologies)
- Pedestrian Nagivation
- Ship Navigation
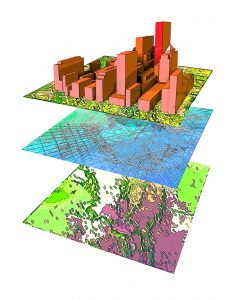
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
These systems are any system that records, stores, visualises or analyses data in relation to it’s position on the planet.
Common examples include:
Google maps – stores and visualises the location of businesses and amenities.
Google trends – Shows what searches are popular on the planet at a particular time/date/location
Weather tracking systems – predict where typhoons are going to track
MCS
Media Communication Systems (MCS)
These systems are more commonly known as satellite TV services. They use satellites to transmit a variety of data and include:
- Satellite Television services
- Satellite Phone services
- Satellite Internet services
Advantages
- An advantage of satellite media communication services is that they can often be deployed with the need to a cable telephone network or broadband service, meaning that they are great for remote areas.
- A single transmission can serve millions of receivers, meaning that they don’t suffer from bottle-necks or service.
Disadvantages
- Signal quality is reduced / halted in bad weather.
- The offer a high download than upload speed

How Satellite Television Feeds work