What are they?

[note title=”Key Definition: Magnetic Storage Devices”]
Magnetic storage devices are any devices that store binary data on magnetically polarised plates or tapes. The pattern of polarisation indicates whether the data stored represents binary 1 or 0.
[/note]
The most common types of magnetic storage devices are:
- hard disk drives (HDD)
- tape drives
- floppy disk drives
How do they work?
Magnetic storage devices store data by polarising the surface of a magnetic disk,tape or platter using a tiny electromagnet. The stored is then read by the read head passing over the magnetised surface and the direction of polarisation is then detected.
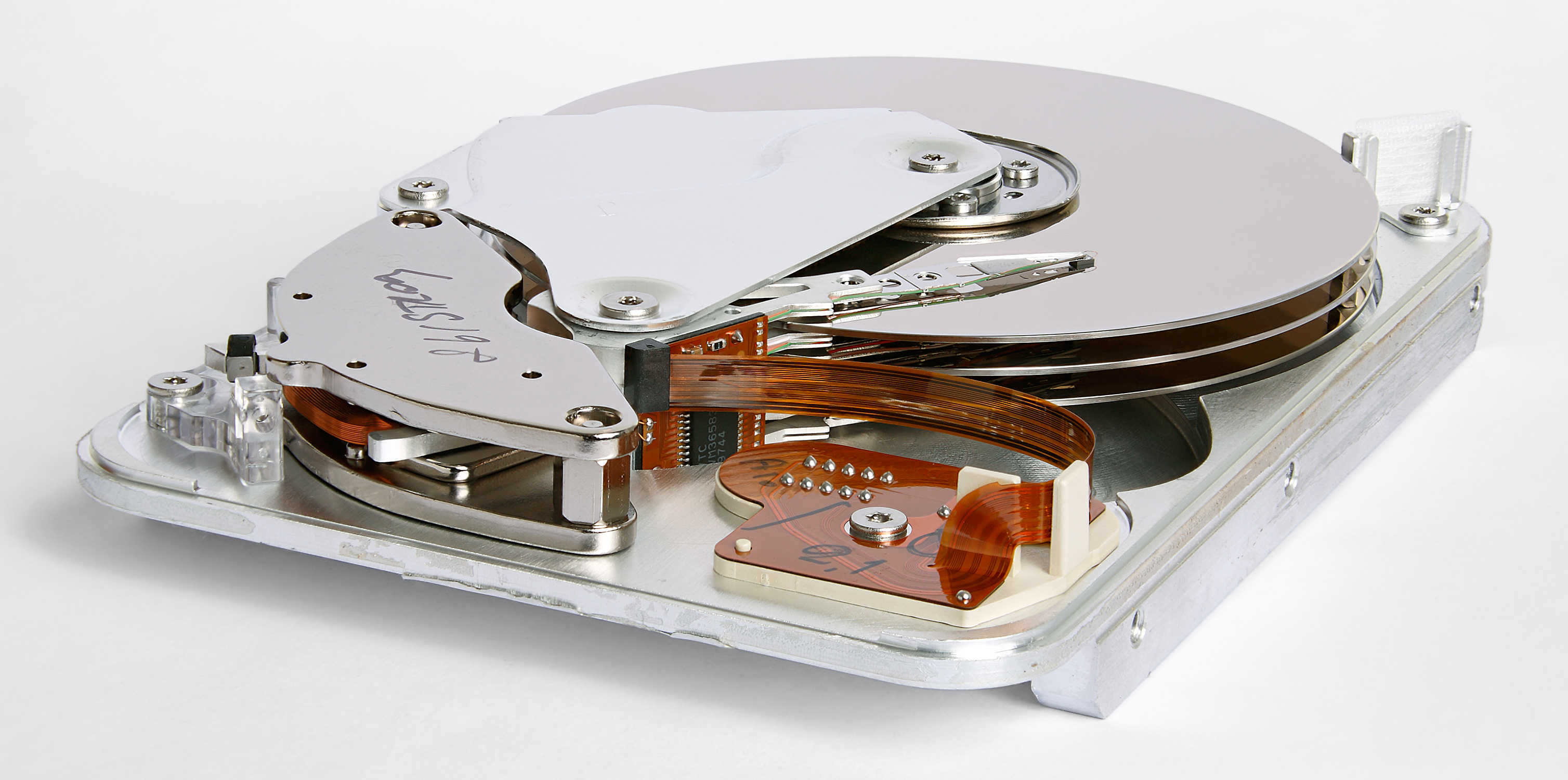

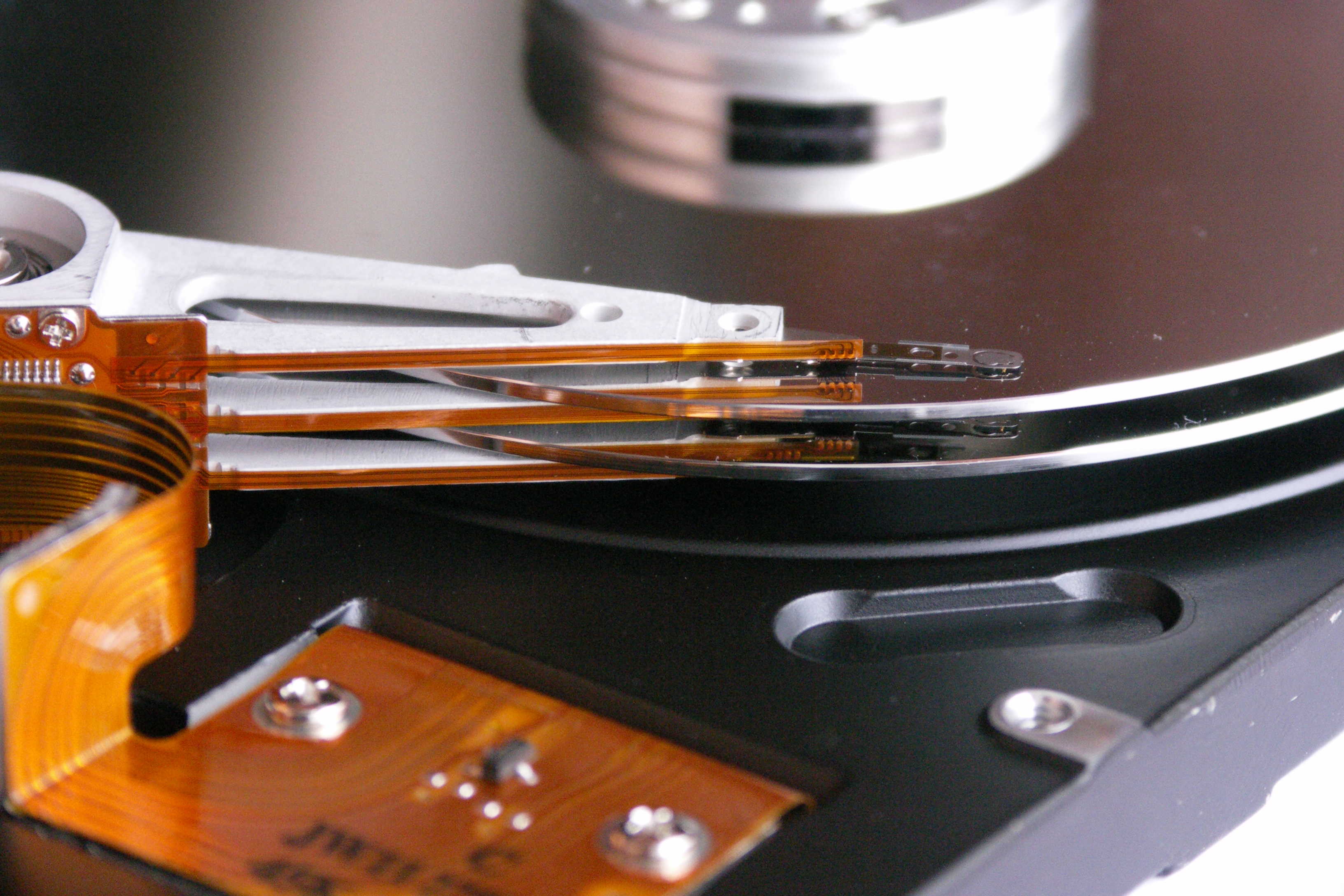
Magnetic hard disks are currently the most common form of storage in desktop and laptop computers(although SSD drives are rapidly catching up!)
Data is store in hard drives on metal or glass plates, or platters.
Advantages
Can you think of any advantages of Hard Disk Drives?
- Relatively cheap per GB
- Reliable long term storage
- Fast access as the actuator arm can move to any point on the platter very quickly
Disadvantages
Can you think of any disadvantages of Hard Disk Drives?
- Slower Read / Write speed than some forms of storage because of moving parts.
- Can fail without warning because of moving parts.
- susceptible to corruption of data if subjected to a strong magnetic field, if dirt gets in the housing, or if the device is dropped.