Sensors
Introduction to sensors
Sensors are everywhere, though we rarely even notice them. Take you mobile phone – how many sensors can you thing of that it has?*
Their job is to alter the electrical signal that is passed through them depending on the value that they are sensing.
For example for a simple Light dependent Resistor (LDR) the resistance within the resistor varies depending on the amount light hitting the surface of the resistor.
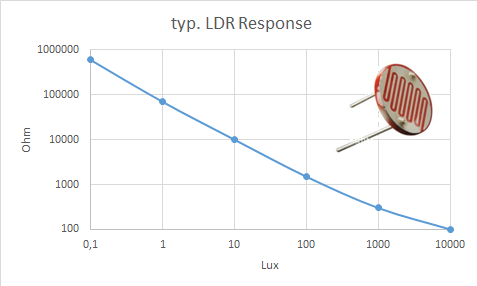
LDR Resitance falls with increased light on the sensor. Source Wikipedia
Digital versus analogue sensors

Digital accelerometer
Simple sensors like the LDR above are analogue sensors. They simply emit a raw analogue signal. This means that the signal has to converted to digital using an analogue to digital converter (ADC) before the signal can be used.
More advanced sensors had a built in microchip that has an in-built ADC that converts the signal to digital before sending the digital signal on to the controlling device. Digital sensors are usually more accurate and reliable, but are more complex and expensive.
*I can think of 7, can you beat me?
Temp
Temperature Sensor
Digital temperature sensor. Source: Wikipedia
Temperature sensors are sensors that detect the temperature. Sometimes this is achieved through contact with the object to be measured, sometimes is it done through measure the ambient temperature of the room or environment.
Contact Sensors
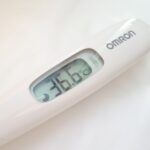
Contact temperatures sensors are used when you want to measure the specific temperature of an object, not the environment it is in. A common example is a digital mouth thermometer. The end of the probe must come in contact with mouth tissues in order to get a reading.
Ambient Sensor
Ambient temperatures are used to measure the temperature of the nearby environment, such as the temperature of a room. They are also used in farms to help with rearing young chicks. The incubator needs to be kept at a specific temperature in order to for the chicks to hatch.
Common uses of temperature sensors
- Ovens
- Car Engines
- Air conditioning
- medical devices
- Night vision googles
- Fish tanks
Light
Light Sensors

Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)
Light sensors measure the amount of light (visible, infra-red or laser light). These sensors have a variety of different applications, including:
- CCD (cameras)
- Barcode Readers
- Optical Drives
- Detecting changes in passive infra-red light levels (see motion sensors)
Analogue Light Sensors
These can be used in a variety of different settings. When connect to a circuit their resistance value changes depending on the amount of light hitting the sensor. They have a wide variety of uses, like controlling a Flappy Bird game wirelessly just by waving my hand.
Passive Infrared Sensor
Passive infra-red sensors detect changes in the amount of infra-red light being emmited within an environment. They are commonly used for security systems to detect intruders.
Image/ Video recording Sensors
These are far more complex sensors that CCD or CMOS sensors to record image or video data. They are also used in optical mice to detect movement of the mouse. To see how they work, watch this video.
Common Uses of Light Sensors
- Intruder detection systems
- Night vision googles
- Automatic street lights
- Image and video recording
- Self driving car cameras
How light CMOS/CCD Sensors work
Motion
Motion Sensors

3 axis accelerometer
Motion sensors are devices that can detect changes in the speed or direction of an object being monitored.
Accelerometer
Accelerometers detect motion by a mass inside the sensor applying pressure to a piezo-electric surface. This causes the signal out from the piezo to change and this change is detected by the device. The can usually detect movement and rotation on 3 axes.
Passive Infrared Sensors
These sensors detect motion by measuring changes in the the amount of infrared radiation being emitted by an object. Mammals give off heat and so these sensors can be used to detect mammals and so can be used in security systems or wildlife tracking systems.
Common Uses of Motion Sensors
- In washing machines to detect when the drum has stopped spinning
- In security systems.
- Used in smartphones to detect phone orientation and movements.
H₂O
Water Sensor
Humidity Sensors
These sensors measure the moisture percentage in the air and usually output a digital signal. They are commonly used farms to control crop humidity.
Moisture Sensor
Moisture sensors are also used in agriculture in order to help maintain soil moisture levels at the correct level.
Common uses of water sensors
- Agriculture to maintain water levels for crops and animals
- Air conditioning when set to dehumidify mode.
PH
PH Sensors
Used to detect the PH levels in liquids and in the soil. Especially important in controlled agricultural environments where adverse PH levels can cause crops to fail.
Common uses:
- In agriculture for help maintaining PH balance in crops
- In food and alcohol production to ensure the correct PH levels
Gas
Gas Sensors
Gas sensors are used to detect the concentration of a specific type of gas in an environment.
Oxygen Sensors
These are highly important in environments where too much oxygen would be fatal, as too much oxygen can be lethal, such as inside oxygen manufacturing facilities or on space craft.
Carbon Monoxide Sensors
Carbon monoxide is a highly dangerous gas that kills thousands of people each year. It is odorless and tasteless and causes immediate drowsiness and can kill within minutes.
They are used widely in any environment where carbon monoxide is likely to build up (anywhere you are burning fuels in unvented area).
Methane Sensors
Used in environments where methane gas levels need to be detected. Methane gas is the gas used in natural gas powered homes (the gas that sometimes powers gas hobs). It is highly explosive and so needs to be controlled, especially in mines where methane gas levels can easily build up to fatal levels.
Common uses
- Smoke & Carbon Monoxide detectors in the home/office
- Inside of factories
- Deep within mines where methane builds up quickly.
- Medical devices for detecting blood oxygen levels.
Magnetic
Magnetic Sensors
There are different types of magnetic sensors.
- Some use coils to detect changes in the magnetic flux density
- Some use reed switches that close the circuit when a magnetic is placed nearby.
- Some use hall elements to detect magnetism.
- Others use different techniques.
Pressure
Pressure Sensor
Pressure sensors can be simple on/off devices, where a signal is sent when the pressure exceeds a certain amount or they can send a signal with the pressure value.
Common uses
- Used in security systems for checking windows and doors.
- Used in pressurized environments, such as airplane cabins or in submarines.
Sound
Sound Sensors
Sound sensors work by detecting vibration causes by audible or ultrasonic sound.
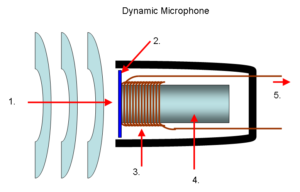
Vibration Sensor (Microphone)
The most common for or sound sensor is a microphone. It works by the sound waves causing a diaphragm to vibrate which in turn moves a bar magnetic through a coil, altering the magnetic field and generating an electrical signal. This signal is measured and converted to digital using an analogue to digital convertor
Common uses
- Audio recording systems
- Used in smartphones
- Security systems
Distance
Distance Sensors

Ultrasonic distance sensor
Ultrasonic Sensors (Short distances <2m)
Ultrasonic sensors are used as distance sensors, mimicking the way in which bats use ultrasound echos to navigate in the dark.
One part of the sensor is the emitter, it emits a steady pulse of ultrasonic sound. The other part of the sensor is the receiver. This detects the reflected signal. As the speed of sound is known then a chip inside the sensor can work out the distance between the sensor and the object being sensed.
Laser Range Finders (Long Distances <5km)
Laser range finders fire a pulse of laser light at an object and measure the time that it takes for the light to bounce off the object and return to the sensor. This time is used to measure the distance to the object.
.
Common uses
- Construction – measuring road distances and distances in engineering projects
- Parking assist technology in cars.
☢
Radiation Sensors
Radio sensors work like a geiger counter, detecting radiation levels either in the ambient environment or an object.
Common uses
- Medical environments such as where xrays are taken to ensure the is no unwanted radiation exposure.
- Industrial environments where radiation is being used.
- Weather monitoring stations where environmental levels of radiation need to be monitored.
Resources
Resources
Past Paper Questions
0478/11 Paper 1 Theory May/June 2016 Qn3
0478/12 – Paper 1 Theory October/November 2016 Qn11
0478/11 Paper 1 Theory May/June 2017 qn 12
0478/11 – Paper 1 Theory October/November 2017 qn 1D
0478/12 – Paper 1 Theory October/November 2017 Qn9
0478/11 Paper 1 Theory October/November 2018 Qn 9
.