LCD Projectors
Liquid Crystal Display Projectors
Can’t access YouTube at school/college? Watch the Google Drive version instead.
How LCD Projectors Work
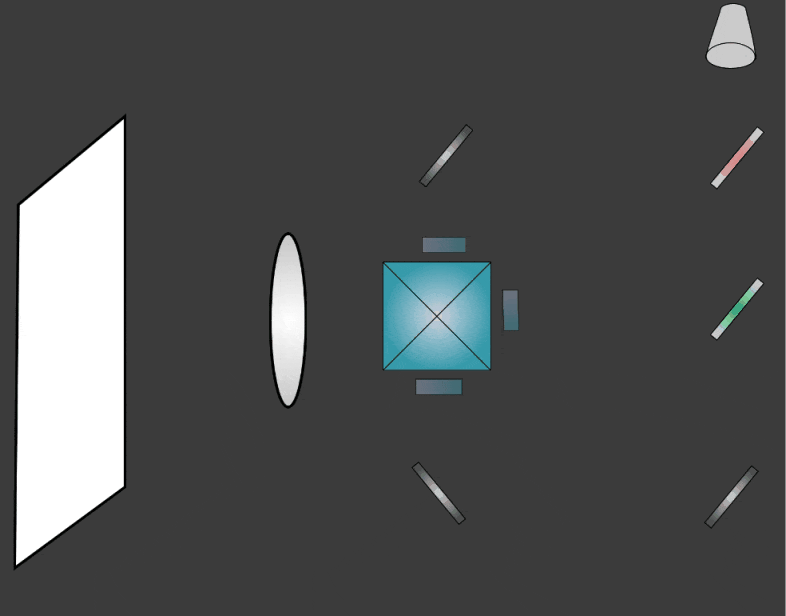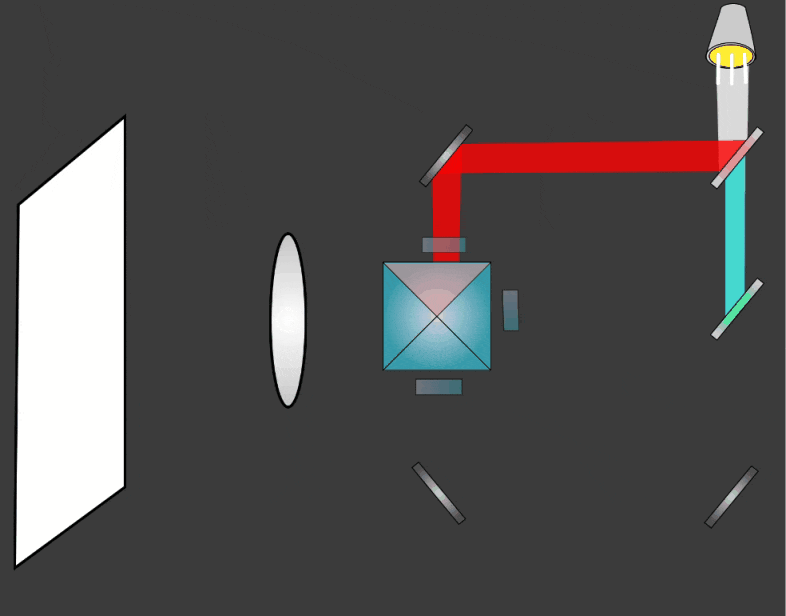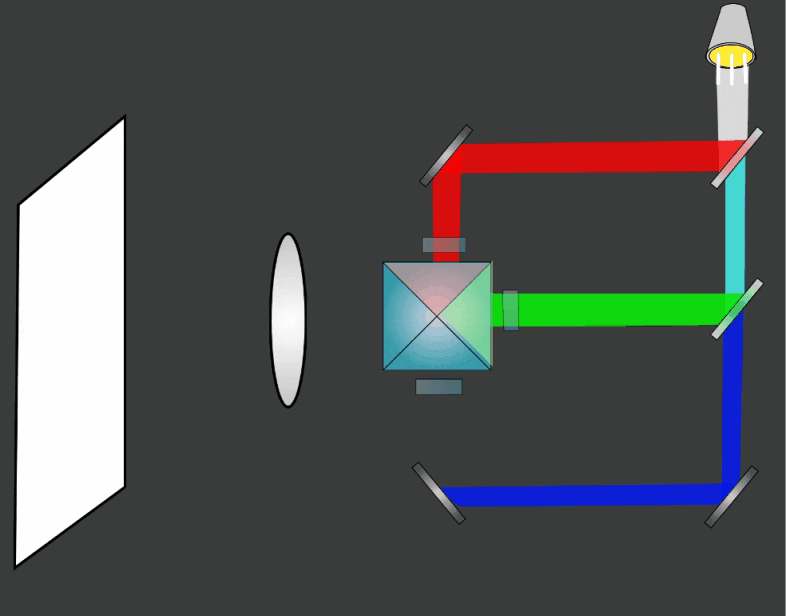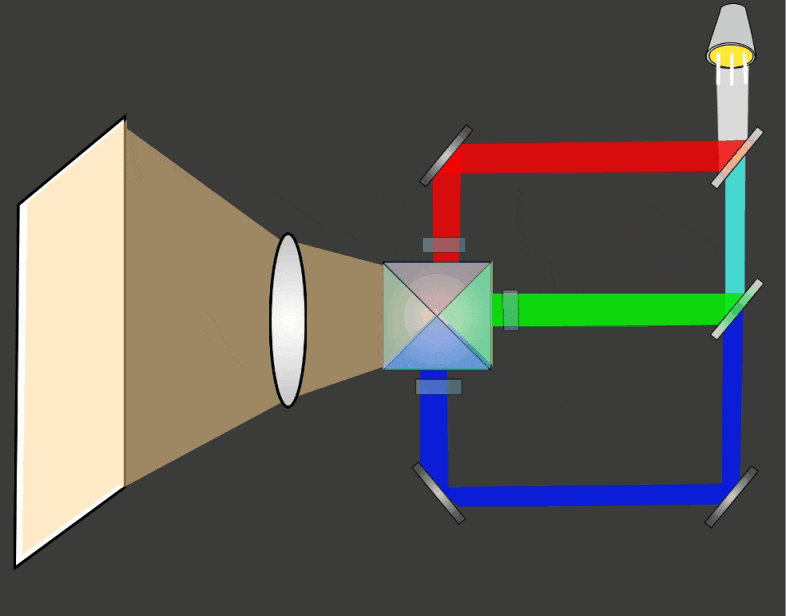
LCD Projectors use a combination of dichroic mirrors and and transmissive LCD arrays to display full color imagery. The basic steps in the process are:
- A single bright light source is split into separate colors (wavelengths) using dichroic mirrors
- The separate colors pass through an array of individually polarised LCD pixels
- The separate colors are combined into a single light source using a dichroic prism
- The light passes through a magnifying lens and is projected onto a separate screen, usually about 3-5 metres from the projector.
LCD Arrays
Liquid Crystal Displays contain a grid of millions of tiny semi-transparent pixels that allow light to be transmitted though, hence they are transmissive by nature. Voltages applied to the individual pixels change the polarization of the pixel and as a result alter the transparency of the pixel.
When light is shone through the array different amounts of light pass through different pixels, this allows an image to be formed. Each red, green and blue channel of the image are created separately and all three channels are combined using a dichroic prism.
The pixels within an LCD array change their transparency depending on the voltage applied.
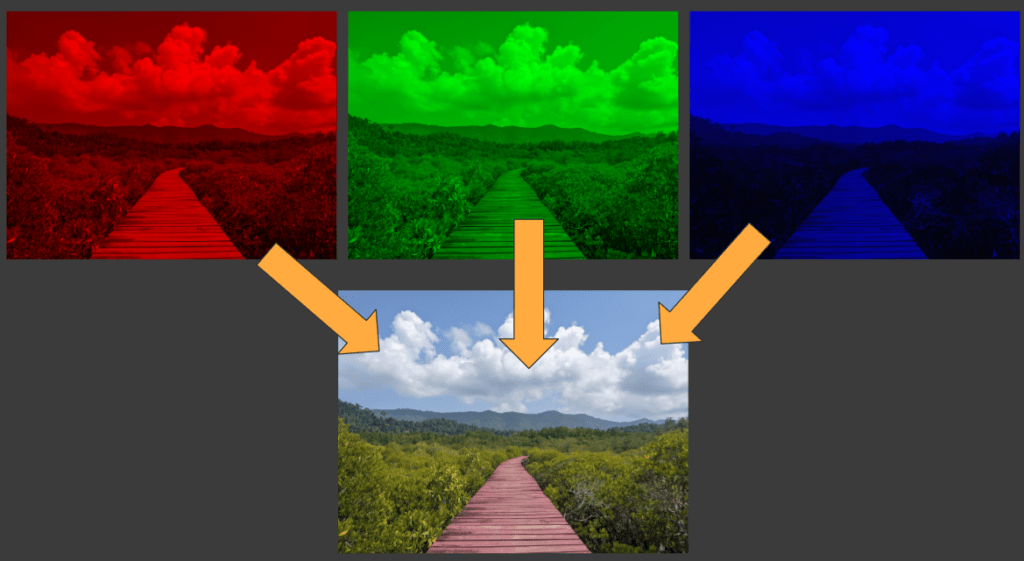
The three separate color channels are combined using a dichroic prism to create a single color image
DLP Projectors
Digital Light Projector
YouTube blocked at school or college? Watch the Google Drive version
Digital Light Projectors use a combination of a spinning color wheel, together with a array of millions of tiny, movable mirrors to produce images and video to be displayed.