Introduction
Flat panel Displays
Flat panel displays are devices that allow users to view a variety of media. They are characteristically thin and fairly light weight, especially in comparison to the older Cathode Ray Tube (CRT) screens that they replaced. Modern flat panels usually use LCD, LED or OLED technology.
Common examples include:
- Televisions
- Computer monitors
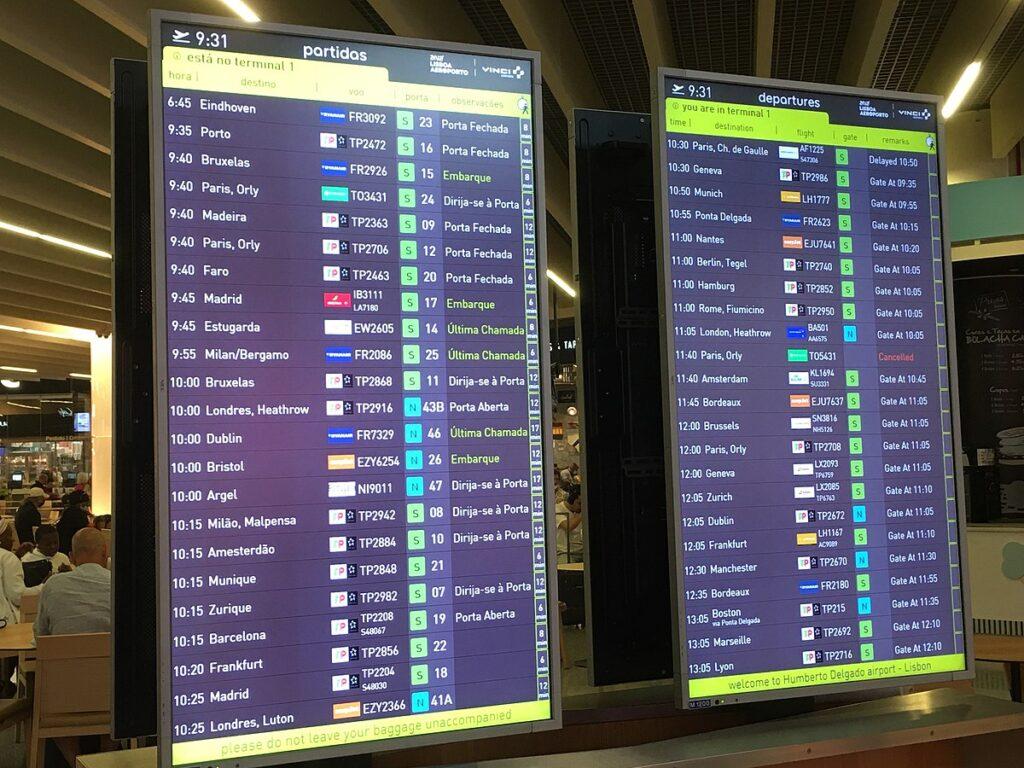
- Airport flight information screens
- Digital signs and advertising billboards
- Ereaders
LCD
Liquid Crystal Displays
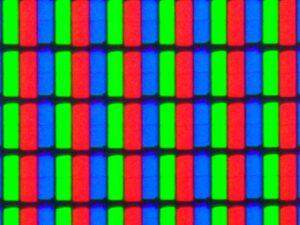
Liquid Crystal Displays contain an array of millions of tiny light filtering pixels. The whole screen has a single light source (or a number of sources) and the brightness of the light emitted doesn’t change. Instead each individual pixel merely alters the amount of light it allows to pass through.
A digital signal is fed from the video source that contains RGB video data. That data is sent to each pixel and when viewed from a distance the RGB lights output combine to form the required color and the full image.
Older LCDs used Cold cathode fluorescent Lamps (CCFL) as the source of backlighting, however they have mostly been replaced by LED backlighting
LED backlighting is superior because:
- They use less power than CCFL
- The are brighter than CCFL
- The LEDs last much longer than CCFL
- CCFL take time to warm up before they reach full brightness.
- Screens can be manufactured that are thinner and lighter than CCFL.
As a result of these improvements most LCD displays are LED LCD displays (not to be confused with LED displays).

The individual pixels are made up a thin layer of molecules in between two transparent electrodes and two perpendicularly aligned filters.
When light is shone through the pixel from behind it would normally travel through the first filter and then be blocked by the second, because the filters aren’t aligned.
The molecules inside the display align themselves in a twisted helix manner and this rotates the light, meaning that some light can pass through. Applying a voltage across the electrodes alters the amount of twist in the helix structure and therefore altering the light being emitted from the filter.
LED
Light Emitting Diode Displays
These are made up of an array of millions of tiny light emitting diodes, each covered in a red, green or blue filter. Each individual diode can be controlled in brightness by varying the input voltage, thereby achieving the desired color and brightness for an RGB triplet of LEDs, when viewed from sufficient distance.
Because each pixel can be controlled individually then they can be turned off completed if needed, meaning that true black can be acheived, unlike LCD displays.
CRT
Cathode Ray Tube Displays
First invented in 1897 by physicist Ferdinand Braun when he noticed that when cathode ray is fired down the length of a tube it cast a shadow on the glowing surface of the tube. If these rays were fired quickly across the screen then an image could be formed.
CRT screens were the main form of display for 100 years, however by the year 2000 they were being rapidly replaced by LCD technology.
Problems with CRT screens
- They we bulky and heavy, due to the cathode ray tube inside. If you wanted a bigger screen, it would also need to be deeper as well.
- They were limited in resolution
- If the same image were displayed on the screen for a long time, permanent ghosting would form on the screen.
These screens are considered legacy devices and it is becoming increasingly rare that you would actually see one still in use.
Comparison
Comparison Between LCD, LED, CRT
Advantages of LCD (CCFL) Displays
- Brighter than LED and CRT
- Lighter weight than CRT
- Cheaper than LED and CRT
Advantages of LCD (LED) Displays
- Cheaper than LED displays
- Brighter than LCD(CCFL) displays
- Use less power than LCD(CCFL) and LED displays
- The LEDs last longer than CCFL
- Lighter weight than CCFL
- Thinner than CCFL
- Achieve maximum brightness quicker than CCFL
Advantages of LED Displays
- Lower power consumption than LCD & CRT
- Can achieve true black
- Lighter weight than CRT
Advantages of CRT
- You can pretend that you live in the 1980s
- You don’t have to worry about your screen getting stolen