Intro
Binary Shifts
Logical Shifts
Logical Left Shift
In a left shift each bit is simply moved to the left with the empty space on the right replaced with zero.
Example
000110
<< 2
011000
Notice the ones have moved along 2 spaces
Logical Right Shift
In a logical right shift the bits are shifted to the right and the most significant bit(empty bit to the left ) is replace with zero. The least significant bit(Any bit falling off the right) is discarded
Example
0011001 >>1 0001100
Some programming languages don’t have an in-built logical right shift, they only have an arithmetic right shift.
Arithmetic Shifts
Arithmetic Left Shift
Arithmetic left shifts work the same as logical left shifts. The bit is shifted to the left (the sign bit is discarded) with zeroes add at the right hand end.
Example
000110
<< 2
011000
Arithmetic Right Shift
In an arithmetic right shift the bit is shifted to the right but the most significant bit is copied to the next most significant bit position on the left.
This is used when the most significant bit is the sign bit (1s/2s Compliment) indicating + / – value. The least significant bit is discarded.
Example 1
1011 >>1 1101
Example 2
10110100
>>3
11110110
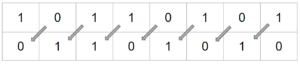
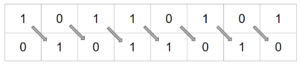
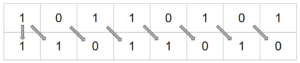
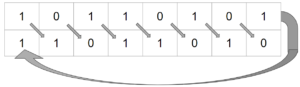
Cyclic Shift
Cyclic Shift
These shifts can be performed either left or right. No data is discarded as the bit that falls off one end is added to the other end.
Example
10110011 Shift 3 Right 01110110
Resources
Resources
Binary Shifts, Bitwise Operations & Binary Manipulation Worksheet
Past Paper Exam Questions
0478/12 – Paper 1 Theory October/November 2016 Qn5