Introduction
Introduction to Encryption
What is encryption?
Encryption is the processing of scrambled data so that only authorized people can view the contents. Unencrypted data, known as plain-text, is encoded(encrypted) into scrambled cypher-text using an encryption algorithm and a pseudo-random encryption key. The data is then transmitted or stored and when the data needs to be accessed it is decrypted using the key.
Why do we need encryption?
The need for secrecy when storing and transmitting data has been an issue for thousands of years – the Roman Empire used the Caesar-cypher to send messages securely between generals and the Nazis used the Enigma Machine to encrypt their messages.
However it is only since the widespread adoption of computer networks, and especially the internet, that encryption taken a central role in everyday life. Billions of people use the internet everyday for online shopping, banking and email. All of the data for these tasks is send across the internet, a publicly accessible network where data can be intercepted by anyone at any time and any data that is sent in plaintext can easily be read.
It is essential that internet traffic is encrypted, so that when you enter your credit-card details for online shopping or your password for a website, anybody eavesdropping on the network cannot easily access that information.
Symmetric Encryption
What is symmetric encryption?
Symmetric encryption (also know as private key encryption) is a form of encryption whereby the same private/symmetric key is used to both encrypt and decrypt the data.
The plaintext data is passed to an encryption algorithm and the algorithm uses the key to encode the data into cypher-text. This data is then sent to the recipient who uses the same key to decrypt the data.
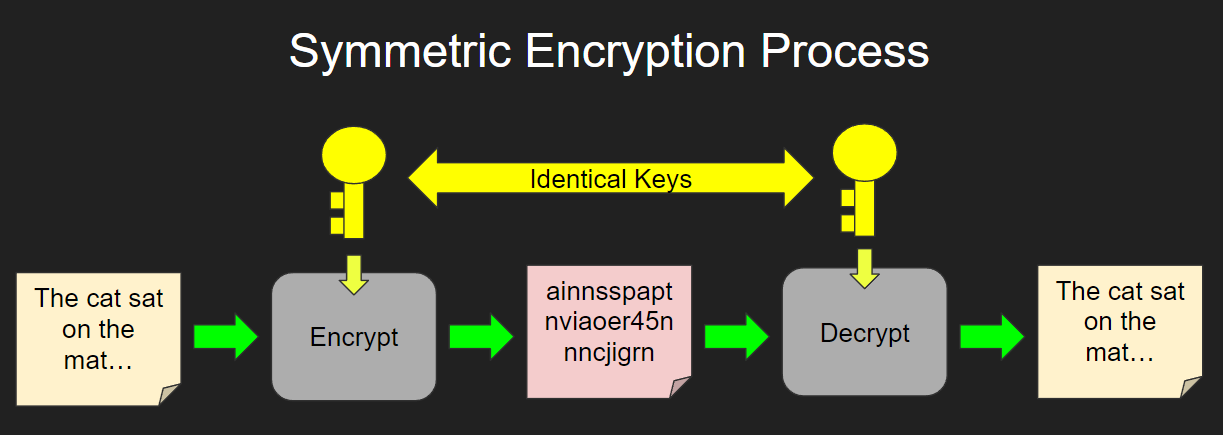
With Symmetric Encryption the same key is used to both encrypt and decrypt the data
This form of encryption is highly efficient and is generally effective as long as a sufficiently long encryption key is used (most websites currently use a 256bit key for standard encryption).
It is important to note that encrypted data is never 100% secure and all standard encryption can be broken through the use of a brute-force attack, given sufficient computing power and time. However breaking 256 bit encryption would require huge amounts of computing power that is beyond the resources of most organisations and therefore is sufficient for everyday transmission of data such as passwords and credit card details.
Pros & Cons
Advantages & Disadvantages of Symmetric Key Encryption
Advantages
- Symmetric key encryption used fairly fast algorithms which use relatively little processing power to encrypt and decrypt data. This makes it very useful when processing large amounts of data
- Symmetric key encryption requires only relatively short encryption key lengths (256bits)
Disadvantages
- The strength of symmetric encryption relies on keeping the key secret. This means the in order to ensure long term security it is necessary to cycle through keys and perform key management.
- Symmetric encryption relies on a pre-shared key between two parties. This makes it unsuitable for secure communication between two parties if they haven’t shared a key in advance – for instance if you log onto an internet shopping website that you have never visited before. In this situation a different form of encryption is required – asymmetric encryption.
Video