Testing
Penetration Testing
Often the best way to find out if your system is secure and to expose any system vulnerabilities, is to employ a white hat hacker to try and break into the system.
They deploy a number of different tools and techniques to try and access the system. Once a vulnerability has been exposed the system can be patched to fix the problem or the appropriate policy be put in place.
Some companies offer hack bounties to hackers. If you can hack their system and prove it you are rewarded with a hack bounty, which can often be tens of thousands of pounds.
Forensics
Network Forensics

If an organisation’s network has been hacked, it is important to learn how and where the breach occurred so that systems can be hardened
If an attacker is successful in accessing a network or computer, Network Forensics can be used to find out:
- Who the attacker is (through their IP address or other information)
- How they gained access to the system, so the vulnerability can be fixed
- What information they accessed
- What their motivates were.
This can be achieved by looking at access logs, using specialist forensic technologies.
Policies
Network Policies
Secure network policies can be highly effective in reducing successful attacks and mitigating the effects of a successful attack.
Good network policies include:
- Forcing users to change their passwords on a regular basis
- Forcing users to pick a strong password
- Restricting user access only to the files / folders they need access to (see User Access Levels)
- Regularly monitoring access to check for suspicious activity
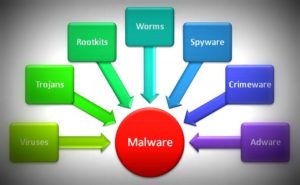
Antimalware
Anti-malware Software
Malware is software that contains features or extra software that either compromises a system or in some way impairs the user’s experience.
Examples include:
- Installing browser add-ons that redirect web traffic via adverts.
- Installing extra software that turns your computer into a bit-coin miner, costly you money in electricity
- Installing software that allows governments or organisations to spy on you, tracking you browsing habits.
Anti-malware detects, disables or removes harmful software.
Firewalls
Firewalls
Any computer or device connected to the internet is vulnerable to unauthorised access. In order to reduce the number of attacks a firewall is used to detect incoming and outgoing traffic and destroy suspicious packets that don’t meet the firewall’s rules.
These rules often:
- Block traffic from known bad IP addresses (or block and entire range of addresses that originate from certain areas)
- Block access to certain ports.
UAL
User Access Levels
An effective way of preventing and containing threats to networks is through the use of User Access Levels.
Each user is given access rights(permissions) to the areas of the network.
Each right is limited to:
- read (view files)
- write(edit files)
- full control(delete/add files)
This means that if an account is compromised, only certain areas and resources are exposed.
Passwords
Passwords
Enforcing strong passwords using network policies are an effective way of reducing the possibility of successful network attacks.
Strong passwords
- Mixture of lower and upper case letters.
- Include a number
- Include the use of characters e.g “£$%^&
- Make sure that standard words are not used on their own. (dog)
- Make sure the password is long enough to prevent a brute force attack.
- Change passwords regularly
- Use different passwords for different accounts
- Don’t use easy to guess passwords (password123)
Limited Login attempts
- Users are limited to a certain number of login attempts, after which their access is suspended for a period of time
- Especially useful against brute force attacks
Biometric Password
Proxy
Proxy Servers
A piece of network hardware that hides a devices real location and IP Address.
When communicating across the network data is first send via the proxy server where the sender’s IP address is replaced by the proxy server’s IP address before being send onto the destination server. This allows a certain amount of anonymity and security.
Encryption
Encryption
Data encryption is useful for limiting the possibility of data being assessed when being stored or transmitted.
- A strong encryption method should be used when transmitting (WP2 for Wifi).
- Hard drives used to store data should be fully encrypted.
- Messaging services should use end to end encryption.
- Data should only be entered in to sites that use HTTPS / SSL encryption
Resources
Resources
Network Threats and Hardening Crossword
Network Threats and Hardening Kahoot.it
Network Threats and Hardening Flashcards
(Make sure when you print you choose ‘print on both sides’ ‘flip on the long edge’)
Past Paper Questions
0478/11 Paper 1 Theory May/June 2016 Qn 8
0478/11 – Paper 1 Theory October/November 2016 4c
0478/12- Paper 1 Theory May/June 2017 Qn78b
0478/12 – Paper 1 Theory February/March 2017 Qn4 – caesar shift example
0478/12 – Paper 1 Theory February/March 2017 Qn9 – biometric password
0478/11 – Paper 1 Theory October/November 2017 qn7 – firewalls
0478/11 – Paper 1 Theory October/November 2017 qn8b/c – SSL
0478/12 Paper 1 Theory February/March 2018 Qn2 (Antivirus)
0478/11 – Paper 1 Theory May/June 2018 Qn9 (Biometrics)
0478/11 – Paper 1 Theory May/June 2018 Qn10d Proxy server
0478/11 – Paper 1 Theory May/June 2019 qn6
News Articles
https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2021/04/24/pentagon-internet-address-mystery/