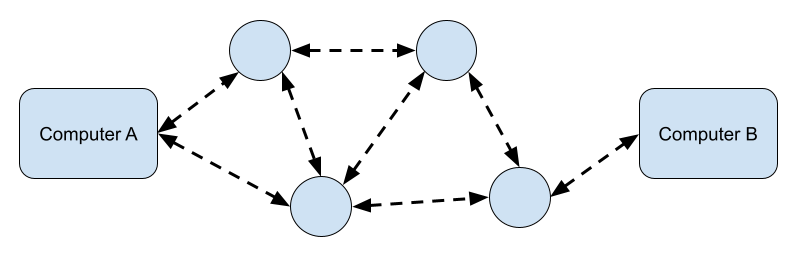
Circuit Switching
Circuit Switching : Connection-Oriented
In circuit switching, a dedicated communication path or circuit is established between the sender and receiver for the entire duration of the communication. This path remains open, even if there is no data being transmitted. It’s a connection-oriented approach.
Fixed Bandwidth
The allocated bandwidth is reserved for the entire duration of the call, regardless of whether data is actively being transmitted. This results in a constant, fixed data rate. Circuit switching is efficient for continuous data streams, such as voice and video, where a constant, dedicated connection is required.
Examples
- Circuit switching is commonly associated with traditional telephone networks (PSTN – Public Switched Telephone Network). When you make a phone call, a circuit is established for the duration of the call.
Packet Switching
Packet Switching : Connectionless
In packet switching, data is divided into small packets that are individually transmitted across the network. Each packet can take its own path to the destination. Packet switching is connectionless, meaning there is no dedicated path for the entire communication.
Variable Bandwidth
Bandwidth is shared among multiple users and devices. The data rate is not fixed, and the available bandwidth is used more efficiently, as it is shared dynamically.
Bursty Data
Packet switching is efficient for bursty data, where data is sent in irregular intervals. It allows for efficient use of available bandwidth.
Examples
Packet switching is the basis for the Internet and most modern computer networks. It is highly versatile and can handle a wide range of data types, from text to multimedia content.