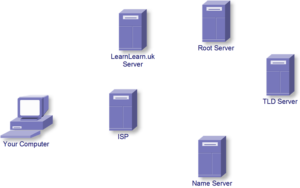
The Internet
The internet is a massive worldwide Wide Area Network(WAN), a collection of millions of Individual Local Area Networks (LANs).
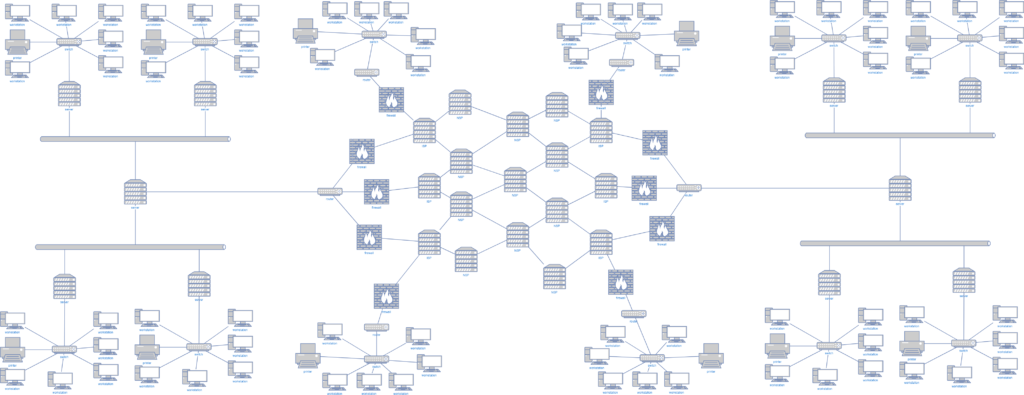
The internet is a massive connected network (WAN) made up of smaller WANs and LANs. A the center of the diagram you can see the central backbone of the internet, a mesh of connected routers.
You can edit your own diagram of the internet and networks at https://www.draw.io/
Just choose New Diagram > Network and pick one of the options.
Public IP Addresses
Each LAN connected to the internet has a single public IP Address. This is the address seen by other computers and networks on the Internet and is the address attached to packets sent across the Internet.
There are 2 main types of Public IP Addresses: Static and Dynamic
Static IP Addresses
These are mainly used by:
- Businesses with LANs that need to be accessed externally from the internet
- Website Hosts
- Gamers who want the fastest, most reliable internet service
Static IP addresses stay the same, which mean that data is always sent in the most efficient manner. However a static IP address opens your network up to attackers.
Dynamic IP addresses
Most home internet users are issued with a dynamic IP address when their router connects to the internet and the IP address is renewed every month or so. Each time it is renewed a new IP Address is drawn from the pool.
This sharing of IP addresses allows the internet to continue to function even when there are more devices in the world than their are available IP addresses (4 billion different ip addresses are available in total for IPV4 addresses). It is also potentially harder to hack as a network’s IP address is constantly changing.
The limited number of addresses available on the internet using IPV4 led to the development of IPV6, though this technology is still in the process of being rolled out…
Private IP Addresses
Computers within a LAN have their own private IP Address, that is different to their Public IP Address. This private IP Adddress is either:
- Issued by the Server / Router using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
- Set manually by the computer user themselves.
Video – How HTML web pages are served
Network Address Translation(NAT)
When a user sends a packet from a computer to a server over the internet, the NAT server swaps the private IP address for a public IP Address and attaches a PORT ID to the packet. The NAT server keeps track of which computers are assigned to which private IP address, so that when a packet returned to the port, it can swap that public IP address on the packet back to the private ip address and send it through the LAN to the correct computer.
Domain Name Servers (DNS)
Packets are sent and received to IP Addresses and all LANs on the great internet WAN have a unique IP Address. However human beings would find it very hard to remember IP addresses for their websites, so instead each website also has a website address. When a computer sends a packet of data to a website (such as a request for a page on a site), it must first find out the website’s IP address. In order to do this it must first send a request to the Domain Name Server asking for the IP address associated with that address. This process is known as a DNS lookup. See the Lesson Google Slides sheet for a breakdown of the steps in the process.
The Cloud
When your data is stored in ‘the cloud’, it is not stored on a server in the atmosphere, but rather on a physical server on someone else’s premises.
Advantages of cloud data storage
- Data is not lost if you have a fire or flood on your premises, or if your laptop is stolen.
- You can access your data from any internet connected location of the planet.
- Cloud storage companies usually have very robust backup systems in place.
- Cloud storage is VERY scalable, very quickly. Want to increase your storage? Just upgrade your subscription and you instantly have more storage.
- Stored data can be sent and shared very quickly.
Disadvantages of cloud storage
- You are handing over security of your data to someone else – you don’t k now who
- Cloud storage can be hacked from anywhere on the planet
- You don’t own the storage, you rent it.
- You don’t know for certain that your data is secure
- If you have limited or no internet access you can’t access your data.
Warning – The video below contains a bit of graphic language towards the end, viewer discretion required.
Resources