Video
Video Tutorial
Entry Verification
Entry / Input Verification
Input verification is the process of checking that user has entered what the user intended to enter.
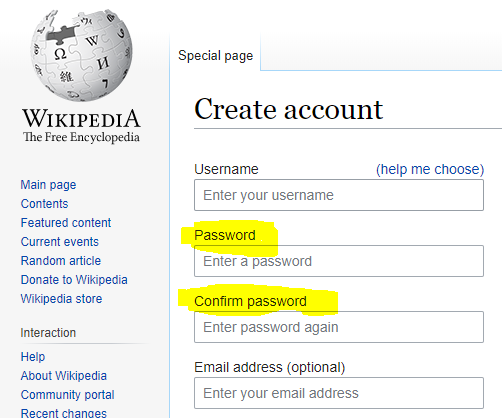
The most common input form of input verification is used in password creation. Whenever you enter a password on website when signing up for an account you are usually asked to enter your intended password twice in order to check that you have entered the same password twice. This is especially important when creating passwords because the inputted characters area normally replaced immediately with ****** so the user can’t be sure that they have entered the intended password correctly twice.
Transfer Verification
Data Transfer Verification
Data transfer verification is the process of ensuring that the data received is the same as the data sent. When data is transferred through a network at each stage there is possibility that data might get corrupted. Therefore when a packet is received it needs to be checked to ensure the integrity of the data. Two common ways this can be achieved is through the use of parity bits and check-sums.
Input Validation
Input Validation
Validation is the process of checking that the user’s input matches the constraints of the system it is being entered into.
Common validation checks include:
Length checks
Check the ensure that the data entered falls within the required length.
Examples:
- Ensuring a password is between 8 and 32 digits long
Format Checks
Check that the correct format has been used.
Examples:
- Ensuring a date is formatted in DD/MM/YYYY format
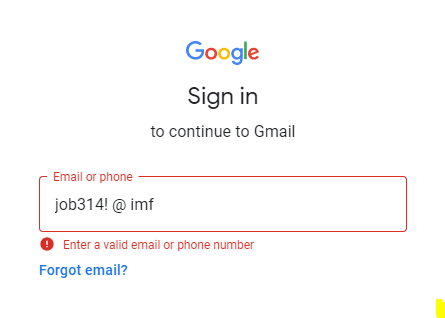
- Ensuring that an email address starts with a letter, has no spaces, contains an @ symbol and a domain at the end
Range check
Check that data in falls within the specified range.
Examples:
- Ensuring that an age is between 0 and 120
- Ensuring that a year is between 1900 and 2020
Presence check
Ensuring that something has been entered.
Examples:
- Ensuring that the user has enter their city and postcode in their address.
- Ensuring that the user has entered their first and last names
Existence check
Ensure that the data entered matches an entry in a list or data table of valid options
Examples:
- Ensuring the the user has entered a valid day of the week.
limit check
Similar to a range check but only focused on one extreme.
Examples:
- Ensuring that a customer does not order more that the maximum amount allowed
check digits(also functions as verification)
Used to check that the user has entered a valid number.
Examples:
- Credit Card Number Check Digits
Password complexity checks
A specific form of format check where an entered password must meet certain criteria.
Examples:
- Must be over 8 digits long
- Must contain mixture of upper and lower care
- Must contain a number and a symbol
- Must not contain the word password or the combination 123
Password history checks
Check that the entered password has not been used before. Note that most good apps/websites do not stored the user’s password, but rather a password hash and so the new password must be hashed before the hash can be compared to previous password hashes.
Example
Example
Here is a trinket example showing both entry verification and entry validation on a email/password signup form.
Resources
Parity Bit Google Sheets Demo (You will have to File > Make a copy to edit it )
Exam Style Questions
- Describe using examples, the difference between data verification and data validation.
- Explain the verification and validation that occurs on a new user email sign-up form.
Programming Tasks
Validation Review Activity (15 – 20 mins)