Introduction
Introduction
Mobile communication standards refer to the set of technical specifications and protocols that define how mobile devices communicate with cellular networks. These standards are essential for ensuring interoperability between different mobile devices and networks, allowing users to make calls, send text messages, and access data services seamlessly across various carriers and countries.
The most common re
- Analog (1G) – The first generation of oldest mobile communication technology that used analog signals, retroactively dubbed 1G.
- GSM (2G): GSM is one of the oldest and most widely used mobile communication standards. It was introduced in the 1980s and operates on different frequency bands, including 900 MHz and 1800 MHz in most parts of the world.
- 3G (Third Generation): 3G is a set of mobile communication standards that marked a significant advancement in mobile data capabilities. It provided faster data transfer rates than its predecessors (GSM and CDMA) and enabled the use of mobile internet services, video calling, and multimedia messaging.
- 4G (Fourth Generation): 4G is the next evolution of mobile communication standards and offers substantially higher data speeds and lower latency than 3G. It allowed for faster and more reliable mobile internet access, which facilitated the growth of mobile applications and services.
- 5G (Fifth Generation): 5G is the latest and most advanced mobile communication standard, providing even higher data transfer speeds, extremely low latency, and massive device connectivity. It enables transformative technologies like augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), Internet of Things (IoT) applications, and ultra-high-definition video streaming.
- LTE (Long-Term Evolution): LTE is a specific technology within the 4G standard that offers enhanced data speeds and improved network performance. It is often used as a marketing term for 4G networks, and many carriers use LTE to deliver high-speed mobile internet.
- Bluetooth: Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology designed for connecting devices in close proximity to each other. It operates in the unlicensed ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) band, primarily at 2.4 GHz.
- Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity): Wi-Fi is a wireless technology that enables devices to connect to local area networks (LANs) without the need for physical cables. It operates on various frequency bands, including 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz.
Analogue (1G) and GSM (2G) are considered legacy technology by EdExcel and therefore you don’t need to know them for the exam.
3G
3G (Third Generation) Wireless Mobile Telecommunications Technology
3G is an older wireless communication technology that provides relatively slow data transfer rates compared to its successors. It was the first mobile data network to enable internet access on mobile devices and allowed basic web browsing, email, and video calling. Maximum theoretical download speeds range from 384 kbps to 42 Mbps.
Pros:
- Widespread coverage: 3G networks have been established in many regions, providing relatively broad coverage.
- Cost-effective: As an older technology, 3G devices and plans may be more affordable compared to newer alternatives.
Cons:
- Slow data speeds: Compared to 4G and 5G, 3G offers slower data transfer rates, making it less suitable for bandwidth-intensive tasks.
- Limited capabilities: 3G may not support advanced applications and services that require higher speeds and lower latency.
4G
4G (Fourth Generation)
4G is a significant improvement over 3G, providing much faster data transfer rates and better overall performance. It enabled higher-quality video streaming, improved web browsing, and faster downloads and uploads. Maximum theoretical download speeds range from 100 Mbps to 1 Gbps.
Pros:
- Faster data speeds: 4G offers significantly faster download and upload speeds than 3G, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Improved performance: Reduced latency on 4G networks makes real-time applications like video streaming and online gaming smoother.
- Better support for multimedia: 4G networks can handle high-quality video streaming and conferencing with fewer interruptions.
Cons:
- Coverage limitations: While 4G coverage is continually expanding, it may not be available in all rural or remote areas.
- Transition challenges: Some older devices may not be compatible with 4G networks, requiring users to upgrade their devices to benefit from 4G speeds.
5G
5G (Fifth Generation)
5G is the latest generation of wireless communication and offers even higher data transfer rates and lower latency than 4G.
It promises to revolutionize various industries with its high-speed and low-latency capabilities, such as supporting augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and Internet of Things (IoT) applications.
Maximum theoretical download speeds range from 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps or more.
Pros:
- Exceptional speeds: 5G offers incredibly fast download and upload speeds, enabling quick access to data and content.
- Low latency: The reduced latency in 5G networks makes it ideal for applications like AR/VR, online gaming, and real-time communication.
- Capacity for massive IoT connections: 5G can handle a significantly larger number of connected devices, making it crucial for the growth of IoT.
Cons:
- Limited coverage: As of now, 5G coverage is still expanding and may not be available in all areas.
- Infrastructure requirements: Implementing 5G requires significant infrastructure upgrades, which can be costly for service providers.
WIFI
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi is a wireless technology that allows devices to connect to a local area network (LAN) without the need for physical cables.
It is commonly used in homes, offices, public places, and other locations to provide high-speed internet access to multiple devices simultaneously.
Wi-Fi typically operates on various frequency bands, such as 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, and offers data transfer rates ranging from a few Mbps to several Gbps depending on the Wi-Fi standard (e.g., 802.11n, 802.11ac, 802.11ax).
Pros:
- High data speeds: Wi-Fi can provide fast and reliable internet access, especially in local areas where routers are available.
- Easy setup: Wi-Fi networks are straightforward to set up, making it convenient for home and office use.
- Support for multiple devices: Wi-Fi can handle multiple devices simultaneously, making it suitable for households and public places.
Cons:
- Limited range: Wi-Fi signals have a limited range, typically within a few hundred feet, which can be a disadvantage for larger areas.
- Interference: Wi-Fi signals can be affected by physical barriers and interference from other electronic devices, potentially leading to connection issues.
Bluetooth
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology used for connecting devices in close proximity to each other, usually within a few meters.
It is commonly used for wireless audio streaming, file transfers between devices, and connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, and headphones to computers and smartphones.
Bluetooth’s data transfer rates have improved over the years, with the latest Bluetooth 5.x offering speeds up to 2 Mbps.
Pros:
- Short-range connectivity: Bluetooth is ideal for connecting devices that are close to each other, reducing the need for cables.
- Low power consumption: Bluetooth is designed for energy efficiency, making it suitable for battery-powered devices like headphones and wearables.
- Universal compatibility: Bluetooth is supported by a wide range of devices, making it a standard for wireless connections.
Cons:
- Limited range: Bluetooth has a relatively short range, typically up to 30 feet, which restricts the distance between connected devices.
- Data transfer speeds: While newer Bluetooth versions have improved data speeds, they still cannot match the speeds offered by Wi-Fi or cellular networks.
- Connection interference: Interference from other Bluetooth devices or wireless signals can affect the stability of Bluetooth connections.
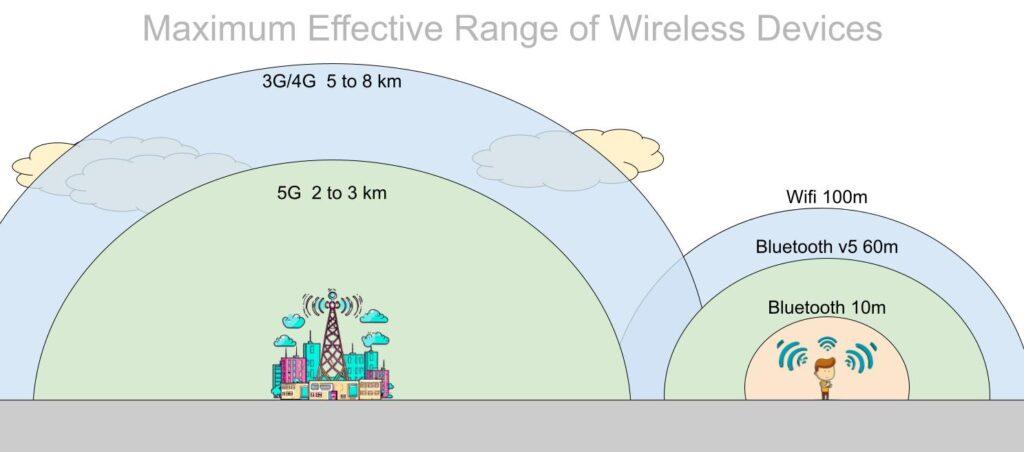
Wireless Range
Range Factors
Factors that affect range
Obstacles
Physical barriers like walls, buildings, trees, and other structures can obstruct the path of wireless signals, weakening the signal as it travels through these obstacles.
Interference
Interference from other electronic devices operating on similar frequencies can disrupt the wireless signal, causing data loss or degradation.
Frequency Band
The frequency band used by the wireless technology can also impact its range. Higher frequency bands generally have shorter range but higher data capacity, while lower frequency bands can have better range but lower data capacity.
Environmental Conditions
Weather conditions like rain, fog, or storms can absorb or scatter radio signals, leading to a decrease in range. Extreme temperatures may also affect signal propagation.
Signal Power
The transmit power of the wireless device or access point plays a significant role in determining the range. Lower power levels can result in shorter effective ranges.
Interference from Other Networks
In densely populated areas, multiple wireless networks can operate in close proximity, leading to interference and reduced range for each network.
Network Congestion
In cellular networks or crowded Wi-Fi environments, increased user density can cause congestion, reducing the effective range and data speeds for connected devices.
Video
4G vs 5G Video
Resources
Resources
Suggested Activities
- Download a WIFI band scanner and see which are the most congested channels where you are.
- Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of 5G technology.
- Explain the concept of WiFi and how it relates to mobile networks
- Explore the uses and benefits of Bluetooth technology
- Create a comparison chart showing the features of 3G, 4G, 5G, WiFi, and Bluetooth
- Design a survey to gather people’s opinions on the impact of 5G on daily life
- Write a short essay discussing the future possibilities of 5G and its impact on various industries
- Build a model or diagram illustrating how 5G networks work
- Conduct a debate on the potential health risks associated with exposure to 5G radiation
- Present a case study showcasing the implementation of 5G technology in a smart city