Introduction
Introduction to Cloud Storage
Cloud storage is a service that allows you to store and access your data remotely over the internet. It enables you to store files, documents, photos, videos, and other digital assets on remote servers, known as data centers, maintained by a cloud storage provider.
The cloud storage process:
- The User Enters Data into the Client-side application
- The application stores the data on the client machine
- The client machine sends a copy of the data to the nearest server.
- This is either done manually as the user requests
- or automatically if data synchronisation is enabled.
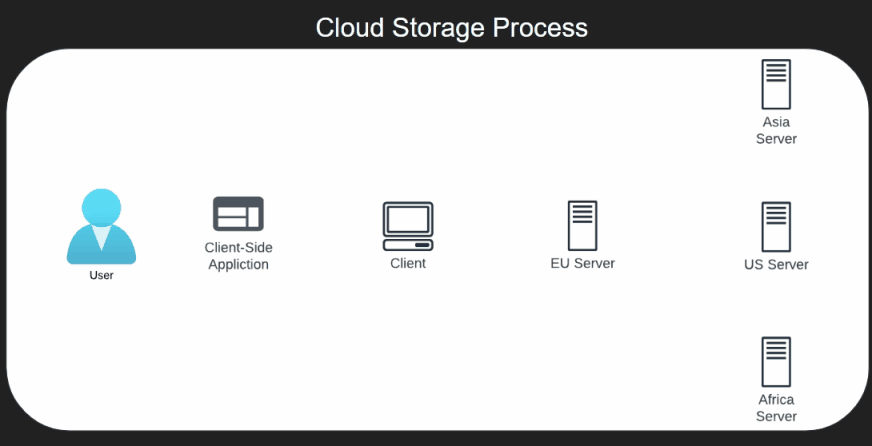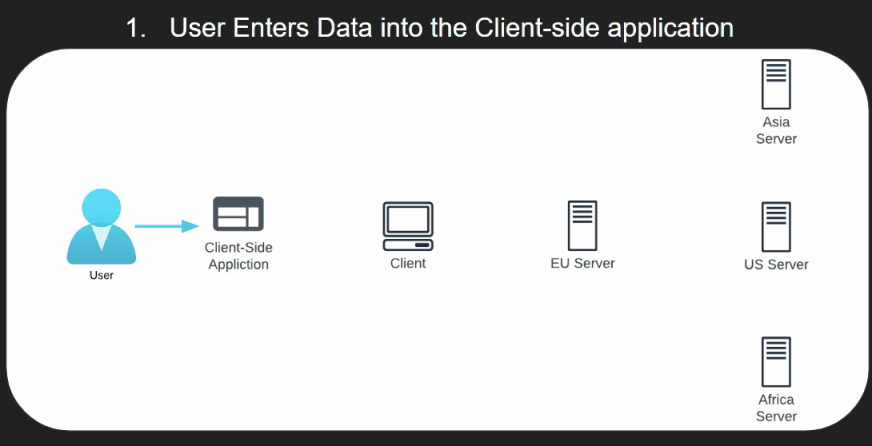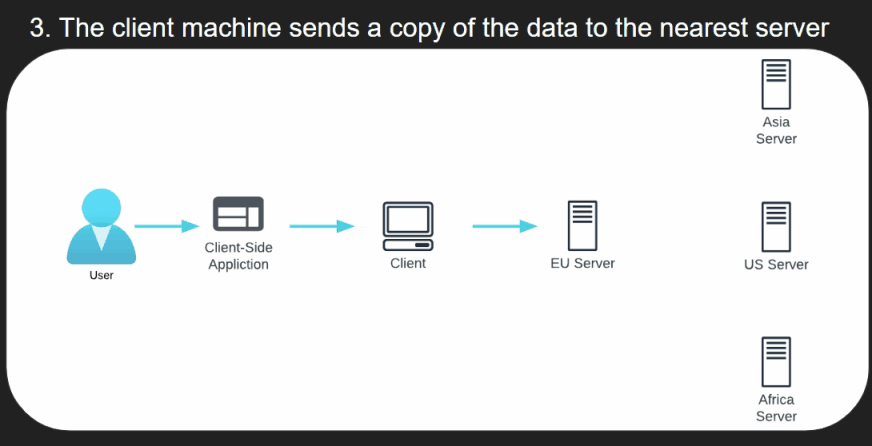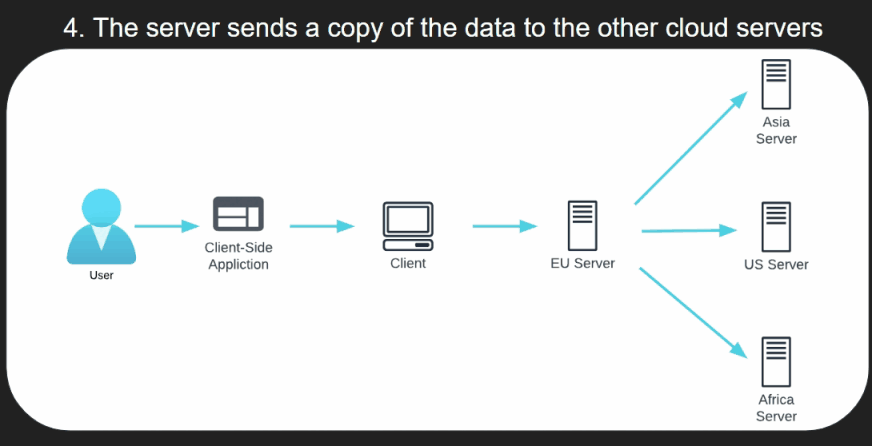
- The server sends a copy of the data to the other cloud servers
Key Terminology
Cloud Storage Terminology
Data Centers
Cloud storage providers have large, powerful servers in data centers to store your data.
Data Replication
Your data is copied across multiple servers or data centers to prevent loss.
Client-Side Applications
You use apps or software provided by the cloud storage provider to upload and manage your files.
Uploading Data
Your files are broken into smaller parts, encrypted, and sent to the provider’s servers.
Data Encryption
Your data is protected with encryption to ensure its security.
Storage and Organization
The provider handles the storage and organization of your data in their infrastructure.
Accessing Data
You can retrieve your files by requesting them through the client-side app.
Scalability
Cloud storage can grow with your needs, allowing you to expand your storage as required.
Synchronization and Collaboration
Changes made to files are synced across devices, enabling collaboration.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Providers offer agreements outlining their commitment to data availability and security.
Pros and Cons
Advantages of Cloud Storage:
- Accessibility: Cloud storage allows you to access your files from anywhere with an internet connection. You can retrieve your data using various devices such as computers, smartphones, or tablets.
- Convenience and Ease of Use: Cloud storage services typically provide user-friendly interfaces and intuitive apps, making it easy to upload, download, and manage your files. You don’t need to worry about physical storage devices or manual backups.
- Scalability: Cloud storage offers flexible storage options, allowing you to increase or decrease your storage capacity based on your needs. You can easily scale up or down without the hassle of purchasing and managing additional hardware.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud storage eliminates the need for expensive on-premises storage infrastructure and maintenance costs. Instead, you pay for the storage space you require, often on a subscription basis, which can be more cost-effective for many users.
- Data Redundancy and Durability: Cloud storage providers typically have redundant systems in place, ensuring that your data is replicated and stored in multiple locations. This redundancy minimizes the risk of data loss due to hardware failures or disasters.
- Data Sharing and Collaboration: Cloud storage simplifies file sharing and collaboration among individuals or teams. You can easily share files with others, control access permissions, and collaborate on documents in real-time, enhancing productivity.
Disadvantages of Cloud Storage:
- Internet Dependency: Accessing and managing your files in the cloud requires a stable internet connection. If you have limited or unreliable internet access, it can impact your ability to retrieve or upload data.
- Security and Privacy Concerns: Storing your data in the cloud raises potential security and privacy risks. While cloud storage providers implement security measures, there is still a small risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. It is important to choose reputable providers and implement additional security measures like strong passwords and encryption.
- Service Outages and Downtime: Cloud storage services may experience occasional outages or downtime, which can temporarily restrict access to your data. Although providers strive for high availability, these issues can still occur and disrupt your workflow.
- Limited Control: When using cloud storage, you are entrusting your data to a third-party provider. This means you have limited control over the physical storage infrastructure and data management processes. It is essential to review the provider’s terms and conditions to understand their policies and data handling practices.
- Long-Term Costs: While cloud storage can be cost-effective in the short term, the cumulative costs over an extended period can add up. If you have large storage needs over a long duration, the recurring subscription fees may exceed the upfront cost of purchasing and maintaining on-premises storage.
- Data Transfer Speed: Uploading or downloading large files to and from the cloud can be time-consuming, especially if you have a slow internet connection. This can affect your productivity and efficiency when working with large volumes of data.